Carnations are great for cut flowers. Due to its excellent keeping quality, a wide range of varieties selection, and Carnations can withstand long-distance during transport qualities farmer attract towards Carnation cultivation.
They are especially the demand for Valentine’s Day, Easter, Mother’s Day, and Christmas. India has an excellent prospect of developing good quality Carnation, cut flowers, Places with cold climates such as Shimla, Kulu, Manali, Kalimpong, Ooty, Kodaikanal, Bangalore, Pune, Nasik, etc.
Mostly Carnation is exported into Europe.
Carnations crops grow in every climate. In temperate zones, mostly in glasshouses, in subtropical places, in polyhouse and glasshouses.

Carnation varieties
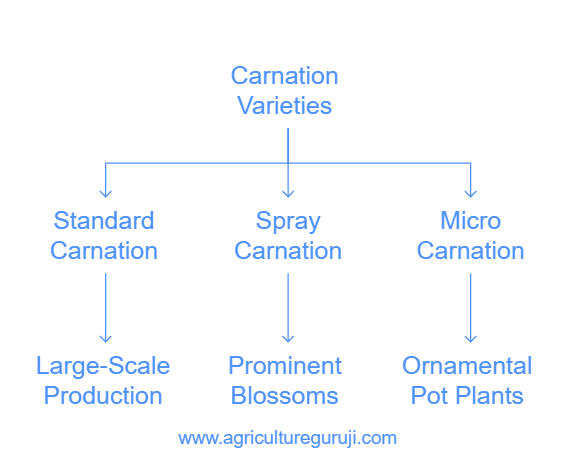
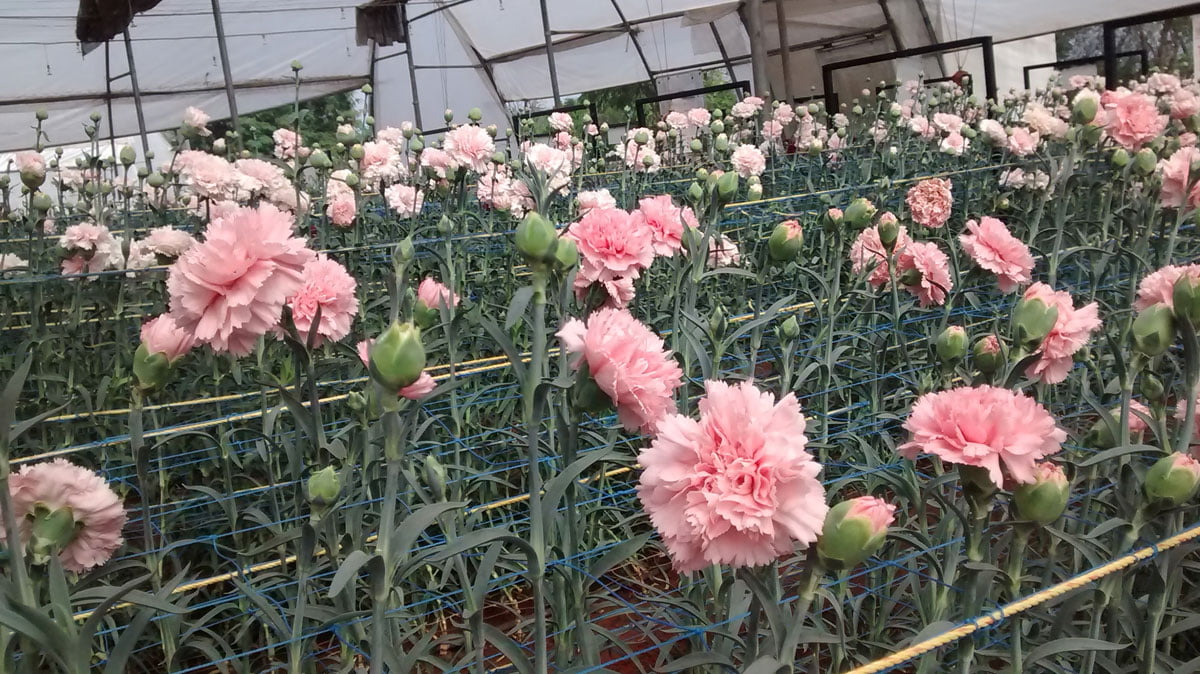
1. Standard Carnation varieties
The standard carnation has one big flower on a single stem. It is cultivated for large-scale production.
2. spray Carnations varieties
The spray carnation has many shorter branches with more prominent blossoms on every branch.
3. Micro Carnation varieties
These carnations have shorter stems and greater production than spray varieties. Micro carnation is used as ornamental pot plants.
Soil requirement for Carnation Cultivation
Carnations cultivation could be a success in any kind of soil, but the soil must be well-drained. The best EC during the vegetative phase is 1.2 mS/cm. And throughout the generative period is 1.5 to 1.7 mS/cm.
A rich sandy loam is an ideal soil carnation. organic matter or compost used to improve productivity
Disinfection of Soil
Before plantation of Carnation cultivation, disinfection of land is needed.
The different Procedures of sterilization are :
- Steam: Not possible for Indian
- Solarization: Cover the ground with vinyl for 6 – 8 months. Sunrays will heat the dirt, which will kill many parasites.
- Chemical – chemical like Hydrogen Peroxide with silver is used
Hydrogen Peroxide with silver
- wet the beds with irrigation water.
- Mix water with hydrogen peroxide at a rate of 35 ml per/lite.
- Apply this solution evenly on soil beds. Use one liter of mixed solution ( Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with silver + water) For the one-meter area. After that, in 4 to 6 hours, the crop can be planted.
Advantages of hydrogen peroxide with silver
- Really simple and secure to use with no hazardous effect on human health.
- Affordable.
- Eco-friendly and doesn’t create any harmful effects on plants.
- The plantation can be performed 4 to 6 hours following fumigation.
- Destroys almost any fungal, viral, and bacterial existence in addition to larva and eggs of these pests in the soil.
- Stable in a broad assortment of temperature and pH.
Climate
1) Temperature
Temperature is the Significant factor that affects the development And flowering of carnation. The perfect environment for carnation production needs to have a cold but steady temperature, low humidity, and long days with high light intensity.
Finest grade carnations are made in areas with high light intensity through winter, and at the same time, the temperatures during the summer months are mild.
In the case of carnation growing, moderate temperatures are favored. Infection at night is vital for quality. The difference between day and night temperatures should be big enough, and the night temperatures are low enough to raise high-quality carnations.
High night and day temperatures, especially during flowering, contributes to abnormal blossom opening and calyx splitting.
2) light
Carnations need high degrees to generate premium quality flowers. Carnations required a minimum of 21500 Lux natural light intensity for adequate photosynthesis.
3) Humidity
In the first phases of development and growth, humidity should be kept around 80 to 85 percent. Whereas at the complete growth phase, it must be 60 to 65 percent. The hot and humid climate isn’t acceptable for carnation cultivation.
Greenhouse for commercial carnation cultivation
Criteria for selecting the Greenhouse project site:
- very good connectivity to the nearest market
- Electricity provision
- Availability of superior quality of water
- labor availability
- An adequate ventilation area is necessary on the sides and top.
- Circulation side drapes should be stored openly at a slanting position to protect the plants in the rain at the monsoons without impacting the atmosphere.
- To control light intensity, white color shaded net (50 percent) is utilized. Roughly 50,000 lux light intensity is called for on the plant level.
- Employ whitewash to the east, west, and west sides of the greenhouse to shield plants from glowing light intensity through the summer season.
Support Method
Great support substance is vital for the achievement of this farming. The carnation crop required 5 or 4 layers of service material.
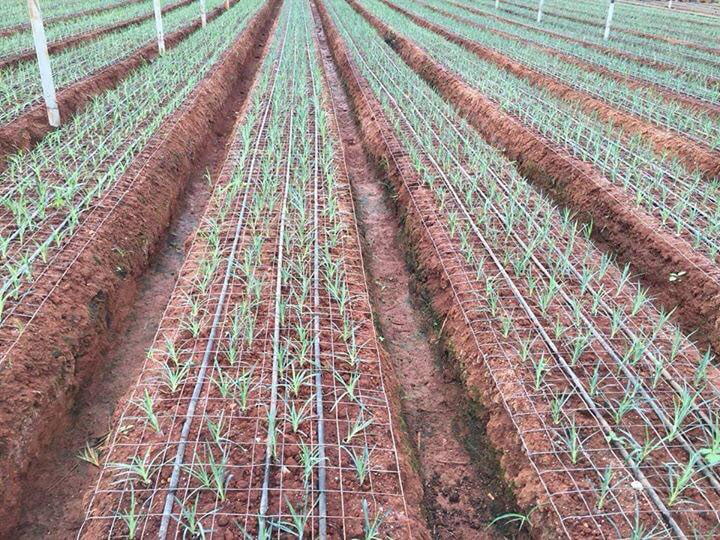

If the carnation crop isn’t supported well enough, then it is going to collapse. This will cause bent stalks and stagnation of this harvest growth. For support, the material is the metal cable, or plastic rope is used.
The carnation crop grows on a raised bed 20 to 25 cm. This will improve better drainage capacity.
To make the more favorable growing condition for carnation organic matter ( FYM) is added in bed with the basal dose of NPK fertilizer.
Bed material composition
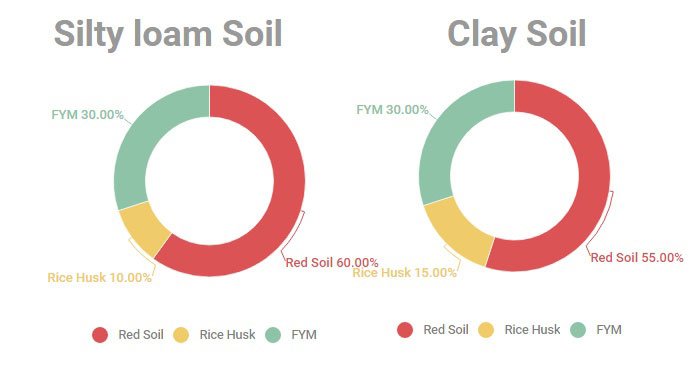
Basal dose :
Neem cake (@1 kg/m2) should Be implemented after fumigation in Bed prep as a preventative against nematodes.
Carnation cultivation
Checks the EC and pH of the soil after use of basal dose and before the plantation. EC needs to be 1mS/cm.
buy a carnation plant from a renowned high-tech nursery like KF Bioplants, Rise n’ Shine Biotech
Carnation plant approximate price is 10rs to 12rs, for one acre 80,000 plants required.
Shallow planting is vital in tropical places. Place the netting on the beds prior to planting—ideal requirements for planting- hot, humid, and a quite bright climate.
Important tips for reducing mortality in Carnation
- The fumigation process is absolutely vital to stop the intrusion of soil-borne diseases.
- The added FYM in bed must be entirely decomposed.
- Don’t offer any high showering. Practice just surface watering and prevent splashing water on the foliage. If overhead irrigation is essential, do it early in the morning if plants will dry fast.
- Never shut the side curtains during the day.
- Adhere to the 21-day program, which basically contains preventative fungicides and insecticides, along with the compounds that improve this plant’s main growth and establishment.
- Don’t postpone the operation. Carry out pinching after two weeks on the 5th foliage set.
Pinching in Carnation

Pinching is a significant cultural performance at the successful creation of excellent quality carnations. After planting, the pinching has been developing a major stem.
If abandoned unpinched, this most important stem generates a “Crown blossom.”
Pinching is a significant function in Carnation, which entails removing the bud-head of the main stem from an early phase. This permits the side shoots to grow. These shoots make the initial flush.
The pinching process means breaking the crop head. The ideal time for pinching is in the morning because the head of the carnation plant easily breaks.
The pinching process starts three months after planting. Spray Captaf or Bavistin (1.5gm/lit) immediately after pinching.
Disbudding in Carnation
The practice of removing undesirable immature flower buds to maximize food for plant development.
for spray carnation variety central terminal bud removed and for standard carnation variety side bud removed
Nets handling
It’s extremely important to raise the nets at the right time.
Raising the net too early, which makes it difficult to choose a crop. Raising too late enables the harvest to fall to one side. After this occurs, stems bend, and harvest losses are unavoidable.
Irrigation system
Throughout the first three weeks after planting, you’ll require overhead sprinklers to stop young plants from drying out.
Later, it’s possible to change to drip irrigation slowly.
Drippers should be put at a distance of 30 cm with 2 Iph discharge for sufficient supply.
Full-grown carnation crop consumes 6 to 7 liters of water per m2 every day.
Fertigation
Create a soil analysis before planting.
Weeks provide only water (no fertilizers) because carnation plant roots are not able to consume any nutrition.
Start Fertilization from 4th week onwards until 8th week: (Per 1000 m2 Every Day) Each Monday, Wednesday, and Friday
| Fertilizer | Quantity |
|---|---|
| 19:19:19 | 1000gm |
| 0:52:34 | 540gm |
| 13:0:45 | 360gm |
| MgNO3 | 360gm |
| Borax | 180gm |
| micronutrients | 150gm |
Every Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday
| Fertilizer | Quantity |
| Ca(NO3)2 | 1140 gm |
Fertilization from 8th week onwards until 12th week: (Per 1000 m2 every day).Each Monday, Wednesday, and Friday
| Fertilizer | Quantity |
|---|---|
| 19:19:19 | 1160gm |
| 0:52:34 | 480gm |
| 13:0:45 | 2150gm |
| Borax | 230gm |
| Micronutrients | 1130gm |
Every Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday
| Fertilizer | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Ca(NO3)2 | 1140gm |
If possible, have the soil analyzed every Two or Three weeks to determine whether it is essential to alter the fertilization program.
Fertilization out of 12th week onwards until the end of flush: (Per 100 m2 every day).
The perfect water EC during generative growth must be approximately 1.6 mS/cm. Continue using the above before the conclusion of the very first flower production peak.
Subsequently, clean water for one week, no fertilizers. Wash the dirt and eliminate extra nutrients.
Method of giving Fertigation
Fertigation should be provided early in the morning at 6 am for greater use from the plants. Take the recommended amount of fertilizers and then dissolve them in an adequate amount of water.
It’s crucial to provide fertilizers with the recommended amount of water to keep EC optimal. Thus, operating the drip irrigation method for the prescribed time.
After each fertigation, open the flush valve to drain water off out of laterals and sub-mains.
Gently wash out the fertigation system to prevent any kind of malfunctioning.
Disease and pest in Carnation
always maintain Cleanliness, cleanliness environment is vital due to environmental restrictions, spraying application, which requires weekly implementation.
Identifying the disease at the initial stage is important.
The most favorable conditions for fungi are humidity and higher humidity.
Maintaining optimal pest and disease control can be achieved by keeping a regular preventative spraying program.
Don’t spray on weak plants as a result of extreme sunlight sown in a comparatively dry condition.
Diseases :
The significant carnation diseases and their potential control measures are described below.
The disorder caused by Fusarium oxysporum is among the most serious disease
1. Fusarium wilt
Wilting of foliage, often only on a couple of branches, followed by departure. Rotting of the stem below floor level with inner brown streaking extending around the stem.
When pulled, the plant breaks off easily while the company roots stay in the soil. Infected cuttings wilt and die quickly.
Control Measure
- The ideal control measures are dirt sterilization or chemical fumigation of the soil, use of pathogen-free crops, and basic sanitation at the greenhouse.
- Rogue and destroy diseased plants to decrease the source of disease.
- Benomyl or Ridomil @ two gm/lit of water drenching.
2. Butt rust – Rhizoctonia solani
Butts occasionally show a brownish discoloration and breaking just below ground level.
The brown rot can stretch up the stem.
Control Measure
- Plant substance derived from pathogen analyzed stock into the fumigated land.
- proper ventilation, Fantastic drainage, shallow planting increase carnation immunity against R. solani
- Moderate fertility level.
- drenching with fungicide reduce butt rust
- (Bavistin or Benomyl @ two gm/lit) before planting.
- If the infection develops, eliminate infected plants and start Ridomil or Benomyl treatment.
3. Rust-uromyces dianthii
Initial infections appear as pale green shellfish such as swellings, which erupt, releasing red to dark brown powdery masses of spores. The disease is normal under warm, humid conditions.
Control measure
- Avoid leaving wet.
- Rogue contaminated plants.
- Maintain a routine preventative spray program with Mancozeb
4. Grey mould-Botrytis cinerea
Symptoms: Originally, a moist tan-colored blotch grows on petal tips and spreads quickly throughout the petals to make a fluffy grey mold. This disorder could create on cut flowers while in transit.
Control Measure
- Reduce humidity, keep excellent ventilation, and hygiene clinics.
- Avoid injuring blossoms.
5. stem and root rot
Withering and yellowing of foliage, foliage departure, outside browning of stalks, and inner workings in nodes. Stem and root rot might be present. Wet conditions, overwatering, and poorly drained soils prefer developments of this illness.
Control Measure
- Avoid overwatering and poorly drained soils.
- Drenching using Benomyl @ two gm/lit or Rovral (0.5 gm/lit).
- Drench using Thiram @ 3 gm/lit.
6. Alternaria leaf stains
Little purple stains appear on the leaves, stalks, and sometimes on the blossoms. These grow into stains up to 5 millimeters in diameter with brownish middle surrounded by a wide purple margin. Spores resembling black specks grow randomly in the middle of stains.
Control Measure
- Avoid excess moisture from plants.
7. Fairy ring spots

Whitish tan-colored stains up to 5 millimeters in diameter surrounded by a narrow reddish-purple margin. Black pin-head-sized spore masses happen in concentric rings around the surface of those stains.
Control Measure
spray mancozeb and sulfur with 1.5gm/lit and 1gm/lit, respectively
8. carnation mottle virus
Incarnation plant CMV commonly finds viruses. Normally infected crops are symptom significantly less, but some cultivars can demonstrate a mottling pattern on the leaves. It reduces flower production and quality and might cause inconsistent color ethics in the petals. CMV does not have any known rector and can be highly contagious.
Control Measure
Prevention is the only option to control this virus. CMV cannot be controlled by treatment. Use plants derived from pathogen analyzed stock and keep rigorous hygiene practices to lessen the disease.
pest
1. Red Spider Mite
This is a quite serious insect on carnations. Red Spider Mites feed on their leaves’ undersides, suck the sap, and the leaves turn pale, withered, bronze, and reveal severe webbing.
2. Aphids
Symptoms: Aphids suck the sap in the leaves and disfigure the young development. In acute attacks, they abandon tacky residue on the leaves and flower buds. Aphids may be responsible for the transmission Of viruses.
3. Caterpillars
Caterpillars are largely an issue of this carnation bud. They damage the carnation bud completely.
4. Root-Knot Nematode
Leaves are yellowish in severe infestations and Stunted development of plants
5. Thrips
Thrips suck the sap out of the leaves, causing them to turn yellow and patchy frequently with black specks and minor wrinkling, and thrips make streaks on flowers, which makes them unmarketable damaged.
Carnation cultivation Economic:
Carnation Cultivation Economic in 2008 sq/ meter (20 gunta)
| Particular | Details | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Area of Polyhouse | 2008 square/meter | |
| Polyhouse Construction | Polyhous as per NHB norms, GI pipe structure & imported plastic @ Rs. 750 / per Sq. mtr. | 1,506,000 |
| Irrigation System | Drip Irrigation system for plants Fertigation unit, Water Filtration unit | 188,000 |
| Bed Preparation | Bed prepared with Red Soil, Rice Husk, FYM, Sand, etc. | 180,000 |
| Plants | Plant Density: 20 plants/sq.Mtr. Total No. of Plants: 40,160 Nos. Cost per Plant: Rs.14/plant | 562,240 |
| Total Investment | 2,436,240 | |
| cost of cultivation per year | ||
| Electricity | 3.0 unit/day | 50,000 |
| Water requirement | Approximate per year | 50,000 |
| Fertilizers | Water Soluble Fertilizers | 60,000 |
| Labour | 3- 4 labours per day | 250,000 |
| Crop Protection | Spraying | 70,000 |
| Packing Material Transport, Sales Commission | Packing material, and transport | 162,000 |
| Miscellaneous | Maintenance, Depreciation | 226,800 |
| Subtotal | 868,800 | |
| Returns Per Year | ||
| Yield / Plant / Year | 12 | 481,920 |
| Price per flower | avg price 3.25 | |
| Total Returns | Per Year | 1,566,240 |
| Cost of Cultivation | Per Year | 868,800 |
| Net Return | Per Year | 697,440 |
Disclaimer: (The above calculations are indicative only.)





can carnations be cultivated in goa??? in naturally ventilated poly house
yes, sir
you can cultivate carnations.
HELLO SIR,
BULK QUANTITY PURCHASE CARNATION
Hi sir,
Please share your contact details our team will contact you.