Hydroponic Farming is the buzzword today in the agriculture industry; many startups and entrepreneurs are keen to start their hydroponic farms; In this article will learn the basics of hydroponic farming.
Let’s begin,
What is hydroponic?
“Hydroponic” is a Greek word meaning hydro is “water,” and ponic is “work”.
A technique for growing plants in water without soil using mineral fertilizer solutions is known as hydroponics. It is a subset of hydroculture.
The plants instead use a nutrient-rich solution (water) for root and shoot growth.
Dr. W. F. Gericke introduced the technology. He publicly displayed bountiful tomato plants cultivated by this method in 1937 in the United States. This technology further spread across, and fresh vegetables for troops were supplied in Wake Island.
Presently many lands are losing their nutrient values due to the conventional use of pesticides and fertilizers.
Presently, farming is not limited to villages only, and it is proceeding to urban and semi-urban areas where there needs to be more proper land.
Here Hydroponic farming becomes a very useful technology to produce desired crops. In conventional farming, soil acts as a reservoir of nutrients, whereas in hydroponic farming water-based solution provides all the necessary nutrients to the growing crops.
A hydroponic system comprises various tools and equipment that are packed together. The medium that anchors the plants does not have any nutrients. Therefore, hydroponic farmers need to mix a specially prepared nutrient-dense solution with this inert medium to help plants grow.
There are mainly six types of hydroponic systems based on cost input, skill level, space availability, and needed environment access. This can be broadly divided into two groups:
Passive” hydroponic systems:
In this, the nutrient solution is provided to the roots using capillary force action without any mechanical influence. Wick hydroponic system belongs to this category.
Active” hydroponic systems:
In this, some mechanism influence is applied to help circulate the nutrient solution and aeration. Pumps are responsible for providing nourishment and aeration to the roots. Other five types of hydroponic systems belong to this category.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
Wick system:
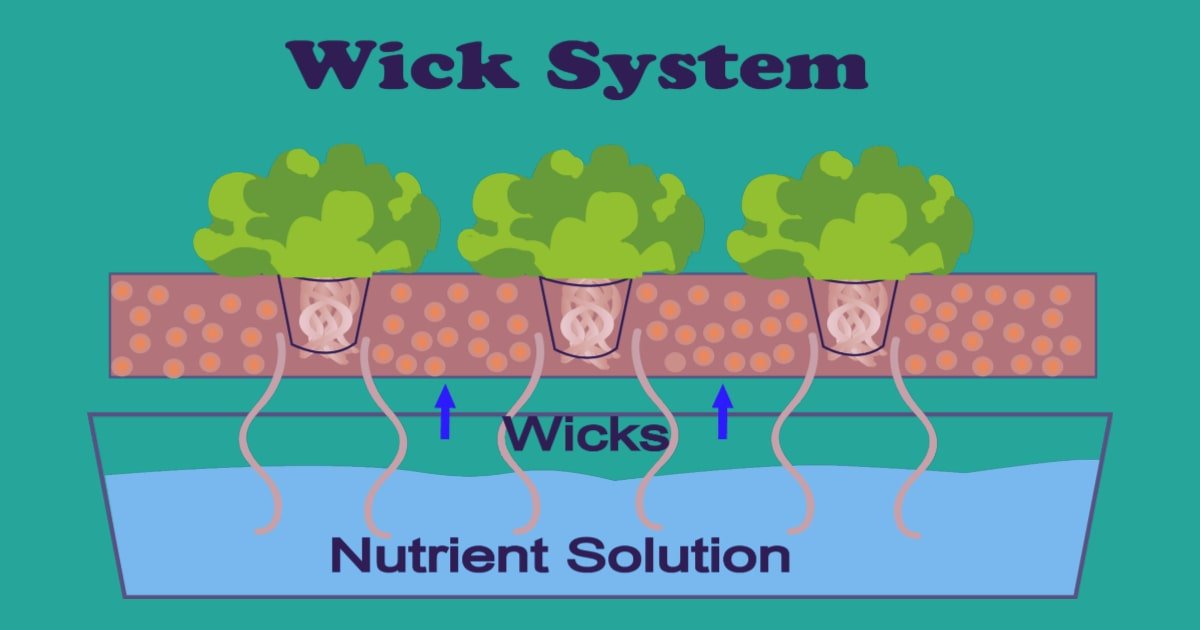
This is the most straightforward hydroponic system that does not require any mechanism for the transportation of nutrients. The wick system operates similarly to an oil lamp. The roots absorb nutrients with the help of cotton or nylon wicks going from the tank to the substrate.
A substrate is a growing media that provide anchoring and aeration to the plant roots. A substrate material can consist of coconut fiber, perlite layer, vermiculite, clay pebbles, lava rocks, etc.
The growing media is accessed in the wick system by inserting one end of the wick through the bottom of the tray or container. The nutrient solution is reached by hanging the other end into a reservoir or container.
Up the wick, the liquid will flow until the medium around the roots is wet. The wick will once more absorb liquid after the medium dries up. Wick systems are best for little plants and are frequently used in aesthetic gardening.
Wick system is not accepted widely because the nutrient solution can become low in oxygen. Alongside this, plants need to be flushed out with plain, fresh water once a week to prevent the deposition of mineral salts that may be present in the growing medium.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) System:
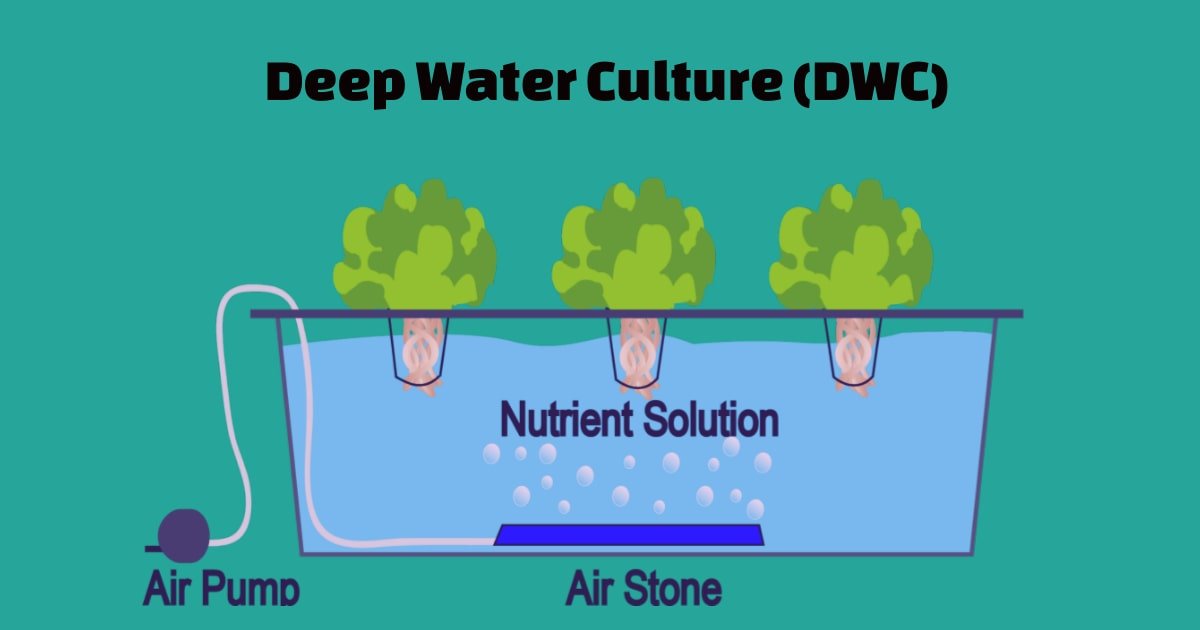
The DWC system is the easiest and most effective type of hydroponic system. In this system, the plant’s roots are constantly submerged in nutrient-dense water to obtain enough oxygen.
The plants are usually fixed on a platform that is often made of foam plastic. This platform drifts in the tank filled with nutrient solution.
A special air pump helps with the aeration of the nutrient solution. Since the plant’s roots are submerged in water 24 hours a day, it is of utmost importance to change the solution regularly to avoid the accumulation of molds and fungi.
The DWC system is mainly used to cultivate small and fast-growing plants, for example, salad and lettuce.
The Ebb and Flow System:
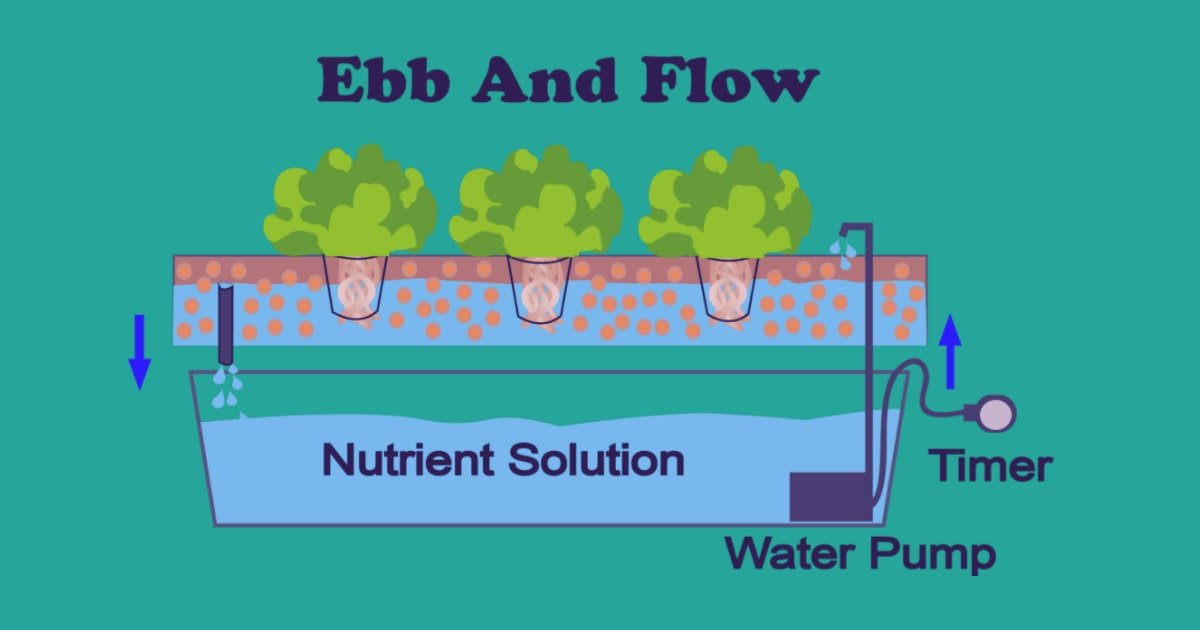
This system is also known as the flood and drain method. The system is widely accepted and requires an intermediate level of skills to maintain.
The plants in this arrangement are kept in a tray that is periodically supplied with water rich in nutrients.
A submerged pump is installed below the tray, which floods the tray with nutrient solution. Once the water reaches a set level, an overflow pipe drains back the nutrient solution into the reservoir.
Oxygen-poor air is pushed out of the root system during the entire flood cycle. When the nutrient solution is drained back, oxygen-rich air is pulled into the growing medium.
As a result, the roots receive enough oxygen and can take in more nutrients.
Gravity is used by the flood and drain system to channel water back into the reservoir for continuous reuse.
The same water can be used for about a week at a time. When it is time to change the water, fresh nutrients are needed to add up.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT):
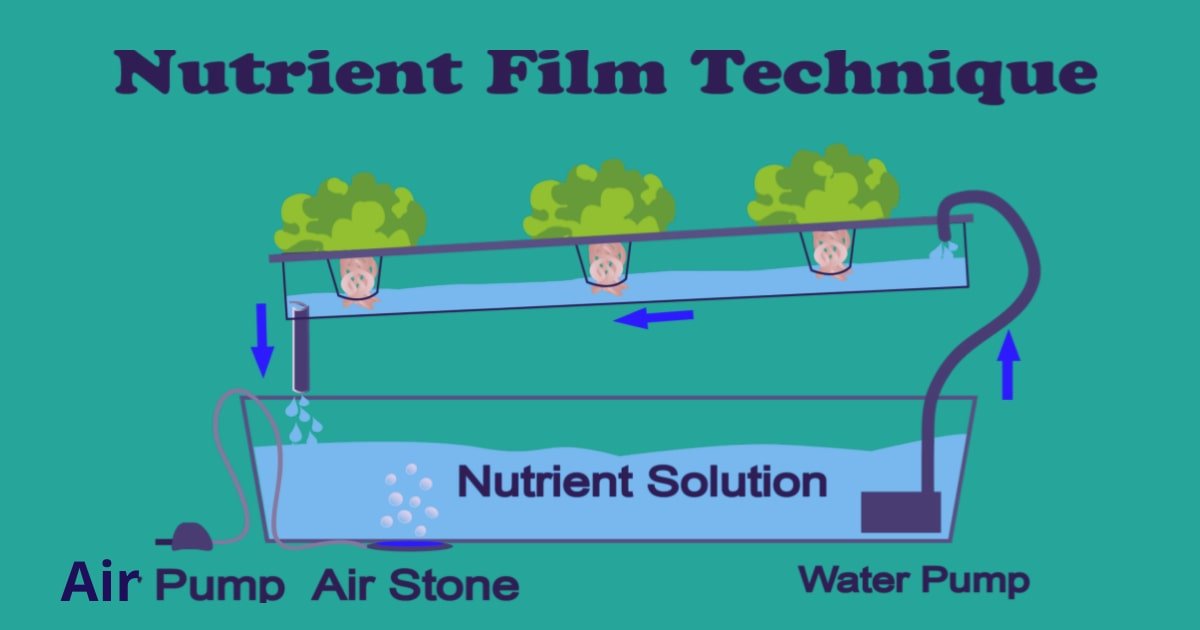
In this hydroponic technique, plants stand in a shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients necessary for plant growth.
As a result, growing tanks housing the plants’ roots are continuously flooded with water. The nutrients the plants require are present in the reservoir.
The plants absorb the nutrients through the root tips when these come in contact with a nutrient-rich solution. The nutrient-rich solution flows with the force of gravity.
The solution’s flow also provides oxygen, which is beneficial for the health of the plant’s roots.
Normally, the grow trays should be tilted to allow for good water flow.The plants are held up by a support collar or a growing basket and no growing medium is used other than air. Hence, the plant can get more oxygen which accelerates its growth.
The NFT technique is best suited for vertical farming, ideal for lightweight , fast-growing plants that do not require much support.
Drip System:
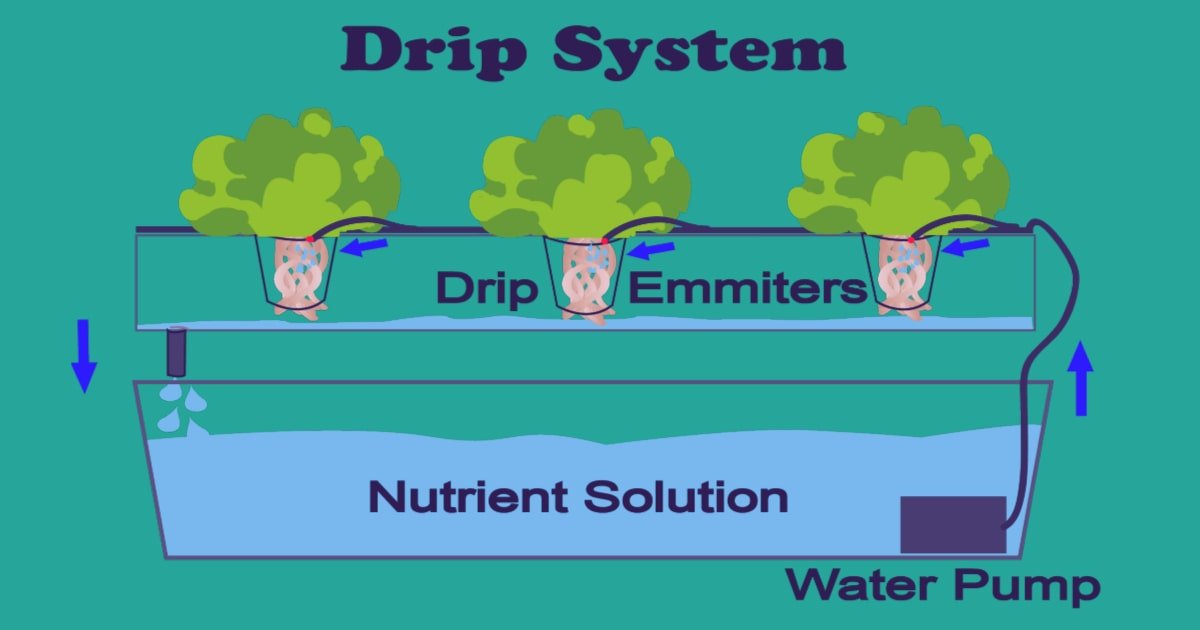
The drip type of hydroponics system works based on the principle of conventional field micro-irrigation technique. Drip system hydroponics uses a system of tubes powered by a water pump to deliver nutrient-infused water to each plant based on each one’s needs.
The pump is usually connected to the timer that automates the irrigation schedule. The drip system transports nutrient-dense water directly to the base of the plants. Therefore, it helps to keep the plant roots moist by reducing water evaporation.
There are two types of the Drip hydroponic system:
a) Recovery Drip System:
This system is also known as recirculating drip hydroponic system because, in this system, the surplus water flows back to the tank and is reused. Any kind of accurate water management plan is not required; therefore, a simple timer can function well.
However, the pH level of the solution should be monitored thoroughly, which may impact the growth of plants.
B) Non-Recovery Drip System.
This system doesn’t reuse nutrient-dense water, so the timer should be set accurately. Otherwise, an oversupply of water can damage roots and result in root rot. There is no requirement to check the pH level of the solution and the nutrient balance as they remain the same. Thus, maintenance is easy. To avoid the clogging of pipes flushing the growing medium with clean water is necessary.
Components of Hydroponic System
A hydroponic setup consists of the following components:
Growing chamber or Tray:
This is a perforated chamber in which plants are grown. The roots of the plants will be submerged in the reservoir containing nutrient solution. The chamber protects the plants from environmental factors like light, temperature, and pest infections.
Reservoir:
The base of the chamber is called the reservoir, which holds the nutrient solution needed for the growth of plants. A reservoir should be made of light-proof material because light can encourage the growth of fungi, molds, and other microorganisms.
Submersible pumps:
The pump helps the transportation of nutrient solution to plant roots. These pumps function as impellers that use electromagnets to spin.
Delivery tubes:
The tube system can be established with either PVC or vinyl materials. The tubing helps the nutrient solution/ oxygen flow to the plant roots.
Air pumps or aerators:
Oxygen is an important element for the growth of plants. Air pumps supply air and oxygen to the nutrient solution, then travel to the roots and plants. Air is pumped through the group of small bubbles which rise through the nutrient solution. Often the air pump is fixed in the reservoir, which helps to increase the dissolved oxygen level in the water, gradually maintaining the overall health of plants.
Grow lights:
Grow lights act as sunlight which emits definite colour spectra of light. The grow lights are available as LED emitters in the market.
Composition of hydroponic nutrition medium
Besides water, the hydroponic growth medium may consist of rockwool, hydrocorn (small clay rocks), coconut fiber or chips, perlite, sand, and vermiculite.
These elements are “inert” and do not react with nutrient solution. The porous nature of these elements helps the supply of nutrients to plants.
However, the moisture level should be checked regularly to avoid the growth of any fungi or molds. Otherwise, it will clog the tubing system, and eventually, plants may die.
The compounds used in hydroponic nutrient solutions
- Ammonium Phosphate – This is used to initiate growth. Phosphorus is crucial for the establishment of the root system.
- Potassium and Nitrogen- These are the primary nutrients of any plant.
- Magnesium is an important component of the chlorophyll molecule, thus green pigmentation. Magnesium sulfate is generally used to fulfill the need; otherwise, a deficiency may result in pale and yellowish leaves.
- Boric Acid- It is used to eliminate unwanted plants, such as brittle stems, dying growing tips, etc.
- Chlorine: Chlorine is provided in the form of Cl ions which is responsible for controlling the opening and closing of the stomata of leaves. Chlorine ions are also required for the water-splitting system in photosynthesis. A deficiency of chlorine can cause wilting and leaf molting.
- Sodium- Sodium in the form of Na ions is needed to synthesize chlorophyll in plants. Sodium ions, together with chlorine ions, help in the opening and closing of stomata.
- EDTA- This element forms chelating ligands with metals such as Cu, Fe, Zn, etc., and this helps the plants’ better uptake of these nutrients.
Which plants can be grown in a Hydroponic system?
- lettuce
- celery
- basil
- parsley
- oregano
- rosemary
- sage
- tarragon
- thyme
- Strawberries
- Potatoes
- Tomatoes
- Mint
- Basil
Plants that take up larger space are impractical to grow in the hydroponic farming system. Such as watermelon and other melons, squash, pumpkin, and corn take up huge space to grow.
Advantages of Hydroponic Farming
Plants can be grown successfully using hydroponics farming techniques, and in the future, it’s anticipated to rank among the most practical sustainable food production methods.
1. Improved Yield and High-Quality production
In hydroponic farming, plants get the required nutrients directly in a solution, which allows them to develop faster growth which results in high yield and high-quality production
2. Reduced Water Consumption
Hydroponic farming requires less water as compared to conventional agriculture; in hydroponic systems, water is reused; thus, the hydroponic system uses very little water
3. Reduced Rate of Pest
Hydroponics farming is done in protective agriculture like polyhouse or indoors, so the chance of pest infestations is very much lower in hydroponic farming
4. Time-Saving System
In hydroponic farming, plant growth is very fast compared to the conventional farming crop life cycle, so we produce a crop in less time.
Disadvantages of Hydroponic Farming
When compared to traditional farming, hydroponic farming is more productive. However, hydroponic farming has some disadvantages, which are as follows-
1. Hydroponic High Set-up Cost
Set-up of a hydroponic system is so expensive.
This is because running a hydroponic system requires various components such nutrient tank, air pump, reservoir, temperature controller, EC meter, PH meter, acidity control, and plumbing systems, and grow light increase setup cost.
2. Requires Hydroponic farming knowledge
A hydroponic system involves a lot of technical aspects.
The system’s tools and procedures require someone with the proper training and experience to use them.
With the necessary knowledge, the plants will probably flourish, which could significantly impact the yield and result in a significant loss.
3. Constant Power Supply Required
Electricity is crucial to the hydroponic farming system’s ability to run all of its parts continually. The entire system is susceptible to failure in the event of a power loss, which might harm the plant’s growth.
4. Constant Monitoring
Constant monitoring is required because, in hydroponic farming, we use Different components to run smoothly. This system all competent and run without fall, so for that, we have Constant monitoring of our system
5. Waterborne Diseases
The plants are in danger of getting several waterborne diseases since water is reused and circulated continuously through the hydroponic system.
The water solution can occasionally spread these illnesses from one plant to another. All the plants in the system might be destroyed due to this.




Hi!
I would love to learn about this system.