Dutch Rose cultivation
Rose is a famous and very beautiful flower; the Rose flower is a symbol of love all over the world. In Greenhouse mostly Dutch Rose variety is cultivated, Dutch rose has high demand in national and international markets. Therefore Dutch Rose cultivation is increasing day by day; also, the Indian government promotes Dutch Rose farming by providing the subsidy.
Direct sunlight affects Dutch Rose productivity. The plant required bright light; hence the Dutch Rose grows very well in the Greenhouse where the climate is in the control condition.

Dutch Rose cultivated mostly for export purposes. In India, Dutch Rose is export countries like Europe, Singapore, Malaysia, Middle East, Australia, and New Zealand.
The Roses plant produces flowers faster during long days ( summer ) than on short days ( winter). This crop required some shading in the summer season, so shade net or painting the polythene from outside the polyhouse.
Basic Essentials parameter for the Dutch rose to grow.
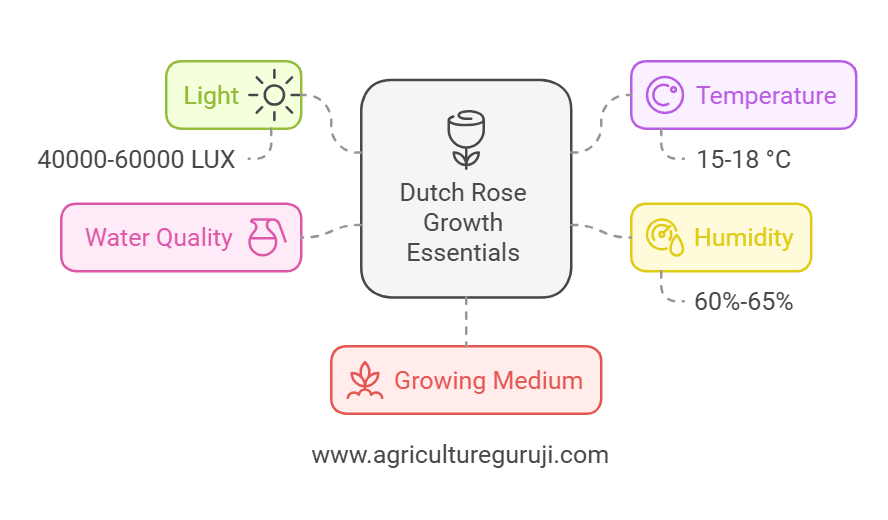
- Light – 40000-60000 LUX
- Temperature 15 – 18 °C
- Humidity 60% -65%
- Good quality water
- Good growing medium
Soil structure required for Dutch Rose cultivation
To succeed in Dutch Rose cultivation, the selection of soil is very important. The main factors to consider are as follows:
- The soil pH should be between 5.5 to 7
- For better root growth and better penetration of roots, the soil should be highly porous and well-drained.
Dutch Rose also cultivated artificial mediums like coco peat, Rockwool, pumice.
Soil sterilization before Dutch Rose cultivation
Before Dutch Rose cultivation, soil sterilization was required, and For Soil sterilization, Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with silver is used.
This method is a very easy, economical & efficient method.
Process:
- Fill the beds with irrigation water.
- Mix water at a rate of 3-7 ml per liter hydrogen peroxide.
(Do not mix any other chemical with this)
Apply this solution evenly on beds; there is no need to cover the soil, and it just leaves the soil; after 4 to 6 hours, the crop can be planted (Use one liter of water for one meter/square area )
Bed preparation Dutch rose cultivation
Raised beds for Dutch Roses cultivation because these beds provide better drainage & aeration for Dutch Rose plant roots.
The dimensions of the beds should be as follows:
- Bed height: 45 cm
- The width of the bed at the top: 90 cm
- The pathway between beds: 45 cm
For Better Drainage Gravel sand is added at the bottom. The soil should be porous.
Organic manure is added to bed because they provide nutritious elements for Plant and help to improve the soil texture.
For better roots establishment, FYM & DAP or SSP ( 10 to 15 gm /sq. meter) is properly mixed on the bed’s upper layer.
Planting
In India, mostly two types of planting material are used; one has budded plants, and the other is a Top grafted plant.
Before plantation, selection of the right dutch Rose varieties & the right color combination is important. It boosts Dutch Rose marketing efforts.
In Dutch Rose red, yellow, pink, orange, white, and bicolor are available, The red colour flower has demand high in the local & export market, on valentine day it is on the boom. Dutch Rose growers earn 20 to 25% of revenue comes from Valentine sales.
Dutch Rose growers select this type of color combination in their Greenhouse.
| RED | 50-60% |
| YELLOW | 15% |
| PINK | 15% |
| ORANGE | 10% |
| WHITE | 5% |
| BICOLOUR | 5% |
The most popular Dutch rose varieties in India.
| Varieties | Colour |
|---|---|
| Top secret/ Taj Mahal | Red |
| Gold Strike | Yellow |
| Corvette | Orange |
| Noblesse | Light Pink |
| Bon Heur | Pink |
| White Avalanche | White |
| Peach Avalanche | Peach |
| Sweet Avalanche | Light pink |
| Tropical Amazon | Orange |
| Hot Shot | Pink |
| Sovereign | Bicolour |
For transplanting, select Dutch Rose plants usually are 5 to 6 weeks old budded plants; Dutch rose plants must be healthy and free from disease with well-rooted development.
Plant density for Dutch is 8 –10 plants / sq. meter. Is suitable.
But Plant density depends upon variety to a variety
Two rows are planted on one bed; the distance between plant to plant is 18 cm, and row – row is 30 cm.
- Row – Row – 30 cm
- Plant -Plant -18 cm
After plantation, humidity at 80% was maintained for 4 -6 weeks to avoid plants’ desiccation.
Cultural Practices for Dutch rose
Cultural practices are performed in commercial Rose cultivation; this will help to high quality & quantity flower; these are as follows:
Mother Shoot Bending
The first flower is pinched after one month from the date of a plantation in after that two- Three eyes bud will sprout on the main branch. These branches produce bud.
When this stage is attained, the plant mother shoots & these branches bend towards the path. Due to this cultural operation, we can get a good quality flower.
Plant Structure Development
When the mother- shoots bend after planting, the first shoot will start growing. This shoot is used for forming a basic and strong framework of plant structure. It was still the entire life of the tree.
All these shoots at the bottom are cut or bent as follows:
- Medium shoot: Cut to other or third leaflets.
- Stronger shoot: Cut the fifth leaf pair.
Bending in roses
Plant leaves are essential for producing nutrients, and bunding needs to maintain an adequate number of leaves on the tree. The leaves are called the lungs of trees.
Weak & blind shoots are select for bending & It is a continuous process and hence carried out throughout the plant life cycle
Remove bud from the branches before bending. It is essential because bud provides shelter for thrips & botrytis
of sprout buds to remove the growing buds for the leaves’ edges. The following bunds of bedding are allowed to grow, and then they are later weakened; they are re-bundled if they are not used for production.
Bending is done off the first or second pair of leaves.
Disbudding
For producing high-quality flower & length of steam side bud on this steam is remove this called Disbudding.
Disbudding should not be done too early or too late.
If done too early, it may be harmful to leaves and, if done too late, affect on upper leaf axil.
the right time to do disbudding when bud attain pea-size and shows a slight color
Irrigation
Water quality should be as follows:
- PH: 6.5 – 7.0
- EC : 0.5 – 1 ms / cm.
Drip irrigation specification-
- Use Pressure Compensating Drippers to uniformity in the delivery of water.
- Use two laterals on one bed.
- The dripper discharge capacity of 1.2 -4 LPH.
After plantation, irrigate the plants with the micro-sprinkler system for four weeks to help uniform root development of the plant, after four weeks that gradually change to drip irrigation.
The Dutch Rose plant’s water requirement can be approximately 800 ml – 1000ml for Per plant per day.
In hot summer sprinkler systems can be used to maintain optimum humidity.
Observes the soil before irrigation and checks the soil moisture.
After that, decide the quantity of water is required for irrigation. It varies with the season, but the frequency is the same.
Always use drip irrigation before 12 p.m
As a thumb rule, the soil should be moderately moist but never having excessive water. To measure how much water is required for Roses is calculate with a tensiometer, pan transcription, or green finger method.
Fertilization
After plantation applies N : P: K 20:20:20 @ 2.5 gm/lit every two days for the first three months.
Irrigate and fertilize frequently in small quantities for optimum results and always care to fulfill the crop requirement.
Applied Micronutrients after every four days or weekly; if crop showing any deficiency symptoms increase the quantity of micronutrients.
If possible, always do the soil analysis every 2-3 months to decide on a specific nutrient schedule.
As a layman, whenever you enter the greenhouse, the plants should look very healthy & glossy.
Harvesting:
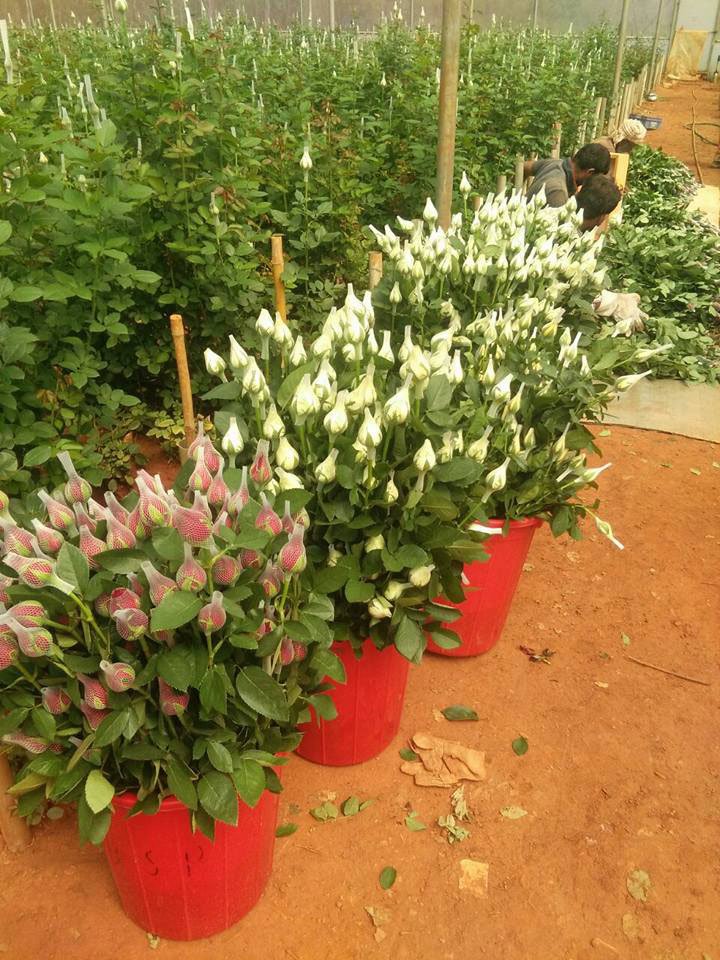

Harvesting start after 12 – 15 weeks of the plantation. The average yield is 230 flowers per sq/meter. (8 – 9 plants) per year.
The cut flower has a minimum vase life of 10-12 days, depending upon the variety. For Harvest dutch flower best time is in the morning or late in the evening, or during the day when the temperature is low.
To produce a big size head, use a bud cap 7 to 8 days before harvesting results in a 10 to 12 percentage bud size increase.
The lower end of flower cut stems is placed in clean plastic buckets containing clean water or 500 ppm citric acid solution.
Read – Economics of Dutch Rose.
Get more information regarding government subsidy on NHB & NHM website.




230 flowers per square meter mean?
After 15 week per day 230 flowers or per year or total crop in 5 years
Hello, Bhoopendra Pratap
Dutch rose plant produces 230 flowers per year in per sq/meter. In one sq/meter area of Greenhouse 8-9 plant grow.
Thanks too much@wud u plz provide me with a fertilizer strategy or program for greenhouse roses for the stage from planting to harvesting time
Hello Fathelrhman
we provide complete guidance on fertigation management on our training cum consultancy program; for more details, please contact 8788462787
I’m thinking of constructing a polyhouse on a leased land. I’m uncertain whether this is possible and wise idea to do this unless polyhouses are movable. Can you advice me in this case –
1. Is there any concept and re-use / movable polyhouse. If not, I need to purchase land first and then construct a polyhouse.
2. What are the sizes of polyhouses. Can we do it in 0.25 / 0.5 / 1 acre ?
Thank you.
Hello Kunal
You can construct polyhouse on leased land. if you wanted more information to ping me on WhatsApp (8788462787) or [email protected]
Sir do you provide training on floriculture
Hello Subham,
Thanks for the comment, please call or WhatsApp on 8788462787 you get details about greenhouse training cum consultancy program.
Sir do u provide training for floriculture I have 9 acres land for agriculture
yes sir,
we provide greenhouse training for more information contact 8788462787
Hii Amar ji
Have you provide greenhouse training program?
Hello Mohit,
yes, we provide a greenhouse training cum consultancy program here we provide complete guidance on how to start Greenhouse farming to its marketing. for more information please contact our customer call centre 8788462787
hi, i am getting green house for lease i don’t no the terms and conditions can you suggest me the right person or i want a one soft copy of lease agreement,
please replay me
Hello Venkatesh,
please contact 8788462787 we provide complete guidance.